
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Mixtures and solutions
Homogeneous mixtures
1) What is a homogeneous mixture?
A homogeneous mixture is the opposite of a heterogeneous mixture:
It is a mixture where it can not be observed different components to the naked eye after shaking.
2) Example of homogeneous mixture: water and syrup
The following figure shows a
mixture of water syrup
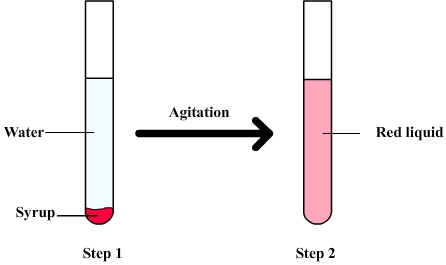

Firstly the syrup is slowly poured into water and tends to sink to the bottom of the test tube ( because of its density ). Water and syrup can be distinguished but after shaking there are only a red liquid whose different component can't be observed separately to the naked eye: It is therefore an homogeneous mixture
3) Other examples of homogeneous mixtures
Water can form homogeneous mixtures with other liquids such as alcohol or ink.
Some solids can be dissolved into water to form a homogeneous mixture. Example: salt, sugar, anhydrous copper sulfate.
Some gases can also dissolve in water as oxygen (essential for aquatic life) or carbon dioxide in carbonated beverages.

©2021 Physics and chemistry


