
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Water
Properties of water in different sates
The essential about water and its different states
The free surface of water
What is a free surface?
A liquid is in contact with its receptacle but also with air. The liquid surface in contact with air is also called " free surface ".
Diagram: free surface of water:
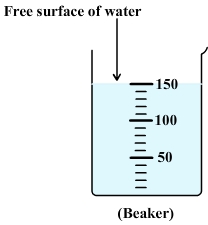
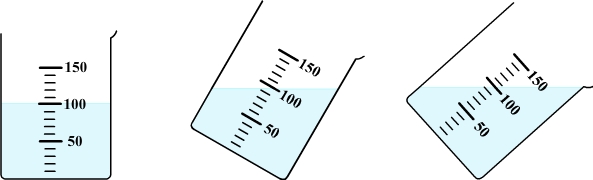
In a stationary vessel, the free surface of water is always flat and horizontal whatever the inclination of the vessel.
Diagram: free surface of water
in an inclined beaker
Properties of the liquids
Diagram: water in a beaker, an
erlenmeyer and a measuring cylinder
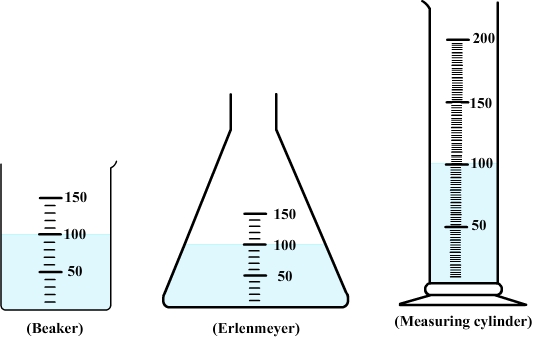
If liquid water is transferred into graduated containers of different shapes, it can be observed that water takes the same shape as its container but keeps the same volume.
Liquid water has its own volume but no own shape.
Properties of solids
If an ice cube is poured from one container to another it keeps its shape and its volume
Solid water has its own volume and its own shape.
Properties of gases
A gas enclosed in a container occupies all available space: it thus has no own shape.
If some air is enclosed in a plugged syringe its piston can be moved to reduce or to increase the volume of the air: air therefore has no own volume.
To sum up:
| Own shape | Own volume | |
| Solid | Yes | Yes |
| Liquid | No | Yes |
| Gaz | No | No |
Comment:
The sand (like other substances composed of powder or grains) has properties that are close to those of liquids.
Each grain has a own shape and a own volume but the sand takes the shape its receptacle: it therefore has no own form (like a liquid).
However unlike liquids, its free surface isn't necessarily flat and horizontal.
Learn more about water and its properties
Basic properties of fluids and definition:
http://www.brighthub.com/engineering/civil/articles/42883.aspx
Properties of gases:
http://www.chemtutor.com/gases.htm
Properties of liquids, solids and gases explained for grade 4:
http://www.nyu.edu/pages/mathmol/textbook/statesofmatter.html

©2021 Physics and chemistry


