
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Mixtures and solutions
Heterogeneous mixtures
1) What is a mixture?
Before studying the heterogeneous mixtures we must first know what's a mixture:
A mixture consists of at least two substances that are brought together in the same receptacle.
Here are some examples:
- Sand and water.
- Oil and vinegar
- Air and water vapor
- Flour, water and salt
etc.
2) Example of a heterogeneous mixture
Before defining a heterogeneous mixture, we will see an example that will help to understand more easily this definition.
This example is that of water and oil.
The
following figure shows a
mixture of water and oil.
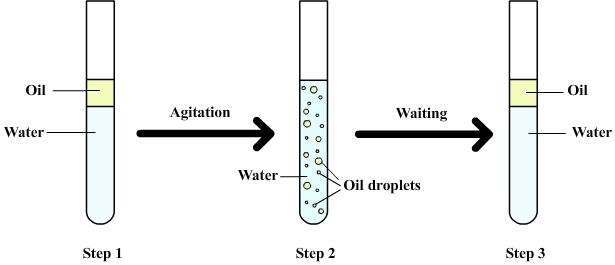
Step 1: Water and oil are introduced into a test tube. Oil stays above the water (it floats) because oil is less dense than water (a phenomenon explained by the buoyancy).
Step 2: After shaking the oil is dispersed in water as droplets (more or less small depending on the force of agitation)
At this point it is said that oil and water form an emulsion.
Step 3: After waiting, all oil droplets finally rise to the surface and re-form the initial layer of oil.
3) Definition of a heterogeneous mixture
A mixture is said to be heterogeneous if at least two of its constituents are visible to the naked eye even after shaking.
These mixtures may consist of:
- Two liquids such as water and oil or water and alcohol.
- A liquid and a solid as the water and sand, water and salt or water and flour.
- A liquid and a gas as in a lemonade exposed to air.

©2021 Physics and chemistry


