
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Mixtures and solutions
Chromatography
1) Usefulness of chromatography
Chromatography is used to separate different colored substances in a mixture in order to determine its composition.
2) Chromatography of a mint syrup: preparation
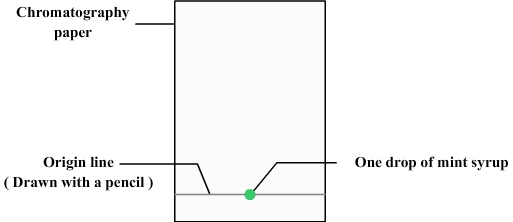
We first need to prepare the chromatography paper:
- The chromatography paper can be simply realized with a retangle of filter paper.
- A line must be drawn at about 1 cm from the bottom (using a pencil because ink can contain dyes that could disrupt chromatography): it is the origin line.
- A drop of mint syrup is deposited with a pipette on the origin line.
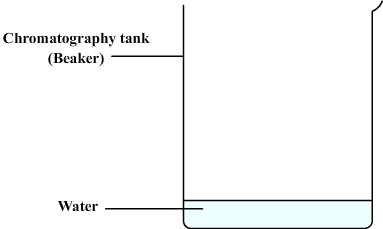
We then prepare the chromatography tank:
- This can be a simple beaker.
- Some water is poured ( about one centimeter ).
3) Realization of chromatography
The chromatography paper must be suspended in the tank and must soak in water without wetting the origin line.
Through capillary action, the water is sucked through the filter paper and rises (such as coffee that rises in a sugar).
The rising water brings with it the drop of mint syrup from which are separated a yellow dye and a blue dye.
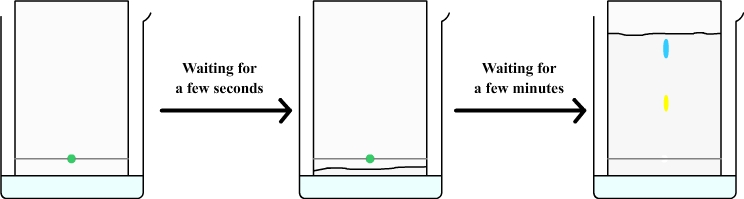
This experiment shows that the green dye from mint syrup is actually a mixture of two colors: a yellow dye and blue dye.
4) Principle of chromatography
The water that rises in the chromatography paper brings with it a blue and a yellow dyes, but yellow dye moves slowlier than blue, they therefore separate and form two distinct spots.

©2021 Physics and chemistry


