
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Atoms and molecules
Compostion of molecules
1) What is a molecule ?
Atoms can gather to form molecules.
Definition:
A molecule is a group of several identical or different atoms linked together.
2) Chemical formulas
A molecule is represented by a formula that indicates:
- The different kinds of atoms within the molecule (Each atom is represented by its symbol)
- The number of each atom (with a subscript after the symbol)
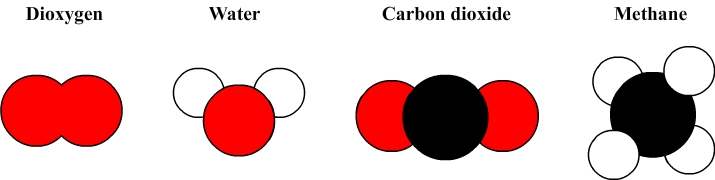
For instance the water molecular formula is H2O:
- The symbol H indicates that the water molecule consists of atoms of hydrogen and its subscript ( 2 ) indicates that there are two atoms.
- The symbol O indicates a water molecule is composed of oxygen atoms but the absence of subscript indicates that there is only one atom.
The water molecule thus consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Some examples of chemical formulas to know:
The molecule of dioxygen: formula O2
The dinitrogen molecule: formula N2
The molecule of carbon dioxide: formula CO2
The methane molecule: formula CH4
The molecule of carbon monoxide: formula CO
The butane molecule: formula C4H10
3) Molecular models
Atoms are represented by models which are colored spheres.
Main models
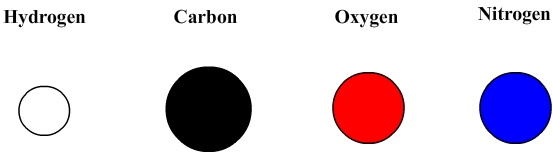

These sphere can be used to build molecules
Some simple molecular models

©2021 Physics and chemistry


