
Chemistry
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online chemistry lesson for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Mixtures and solutions
Distillation
1) How to realize a distillation ?
Distillation setup
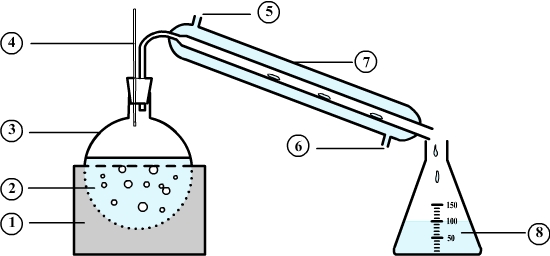

- 1: This is the heating mantle used to heat the mixture to distill
- 2: This is the mixture to be distilled. It is heated to boiling.
- 3: This container is a flask.
- 4: The thermometer is used to control the temperature during the distillation.
- 5: The cooling water enters the condenser.
- 6: The cooling water leaves the condenser.
- 7: water condenser traversed by a cold water from a tap.
- 8: The liquid obtained by distillation is called a distillate.
2) Principle of distillation
The mixture placed in the flask is heated until boiling. The water it contains is then vaporized while the other compounds remain dissolved.
The water vapor passes through a condenser. Water vapor cools and liquefies to form droplets. Thes droplets flow and form the distillate.
All solid compounds initially dissolved in water, remain in the flask.
The distillate also called distilled water is formed of virtually pure water.
3) In which case can it be useful to realize a distillation ?
The vaporization can be used to recover the solid compounds dissolved in water nevertheless vaporized water is lost.
The main advantage of distillation is to obtain pure water.
Comment:
There are more complex distillation techniques that allow separation of liquids.

©2021 Physics and chemistry


