
Electricity
Learning physics
and chemistry
easily and freely - Science for elementary school, middle school and
high school
Free online electricity lessons for elementary school, middle school and high school.
Electrical components
Characteristic curve of a resistor
1) What is a characteristic curve ?
Definition: A characteristic curve is the graph on which are represented the variations in the voltage at the terminals of a component as a function of the current passing through it.
2) How to draw the characteristic curve of a resistor ?
To draw the characteristic curve of resistor we need the following circuit:
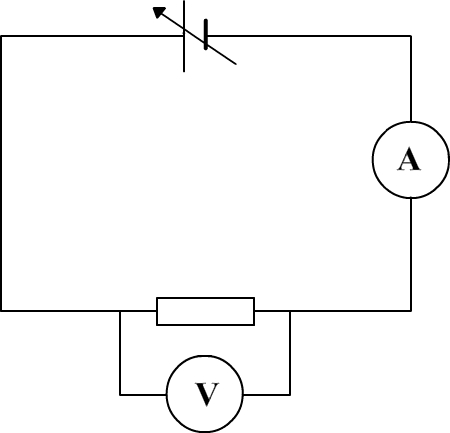
This circuit consists of a battery providing a variable voltage, a resistor, an ammeter and a voltmeter.
If the voltage of the battery changes there is a variation of voltage for the resistor and also a variation of electric current.
The measuring instruments are used to determine several couples of values (voltage and current).
These couples are the coordinates of points used to draw the characteristic curve on a graph with the current on abscissa axis(horizontal axis) and the voltage on ordinate axis (vertical axis).
3) Properties of the characteristic curve of a resistor
The characteristic curve of a resistor is always a line passing through the origin point.
This line indicates that the voltage of the resistor is proportional to the current.
The proportionality coefficient corresponds to the resistance.
example:
For a 10 ohm resistor we obtain, thanks to the measures, the following points:
(I = 0.1 A, U = 1 V), (I = 0.2 A, U = 2 V), (I = 0.3 A, U = 3 V)
(I = 0.4 A, U = 4 V) etc.
These values are used to draw the following graph:
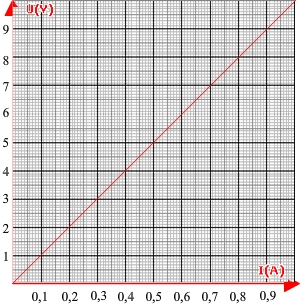
The voltage is ten time greater than current: ten is also the resistance.

| Science class |
Chemistry Electricity Optics Mechanics |
| Electricity lessons |
| Electrical
components -Two-terminal electronic components - Basic electrical components - Diodes - What's a resistor ? - How to determine a resistor value ? - Resistors effects in circuits - How to use a resistor ? - Characteristic curve of a resistor How to build simple circuits and draw diagrams - How to build a basic electrical circuit - How to draw diagrams of electric circuits The electric current - Conductors and insulators - Direction of electric current in a circuit - The dangers of electricity - Current intensity - units how to measure current ? The Voltage - The voltage and its units - How to measure a voltage ? - Voltage in open and closed circuits - Rated current and voltage for a lamp Alternating voltage and current - Alternating currents effects on led - What are alternating current and voltage ? - Periodic alternating voltage and its properties - Oscilloscope - Oscillogram - Frequency - Measuring RMS voltage with a voltmeter Serie circuits - What's a serie circuit ? - Series circuit properties - Short circuit in series circuit - Current law in series - circuits - Voltage law in series circuits Parallel circuits - What's a parallel circuit ? - Some parallel circuits properties - Short circuits in parallel circuits - Nodes and branches in parallel circuits - Current laws in parallel circuits - Voltage laws in parallel circuits Laws of electricity - Ohm's law - Current laws in series circuits - Voltage laws in series circuits - Current laws in parallel circuits - Voltage laws in parallel circuits Generating electricity - Voltage for coil wires What is an alternator ? - Alternating currents and voltages - Generating electricity in power plants Electric power and energy - Electric power and power rating - Electric power received by an electrical device - Electric power consumption by an electrical device - Relationship between - Electric power and energy |
|
|
©2021 Physics and chemistry


